Simplified Pipeline Generation Example¶
As a simple example for a pipeline generation flow, we will reuse the
ExponentCalculator from the
Simplified Analysis Integration Example
to create a pipeline which which computes \(3^{x^2}\) (where \(x\)
is the provided input).
Nodes¶
A Node instance provides a
reference to a particular configuration of some analysis version.
First we need to create a square node:
>>> from django_analyses.models import AnalysisVersion, Node
# Querying the database for our desired analysis version
>>> exponent_calculation = AnalysisVersion.objects.get(
>>> analysis__title="Exponentiation", title="built-in"
>>> )
# Creating a 'square' node
>>> configuration = {"exponent": 2}
>>> square = Node.objects.create(
>>> analysis_version=exponent_calculation, configuration=configuration
>>> )
Now, we could use our square node to calculate \(2^2\):
>>> run_1 = square.run(inputs={"base": 2})
>>> run_1
<Run: #1 Exponentiation vbuilt-in run from 2020-01-01 00:00:00.000000>
>>> run_1.get_output(key='result')
4
Each run will be recorded in the database and returned whenver we call
ExponentCalculator with the same parameters.
>>> run_2 = square.run(inputs={"base": 2})
>>> run_1 == run_2
# True
We also need a raise_3 node for our pipeline:
>>> raise_3 = Node.objects.create(analysis_version=exponent_calculation, configuration={"base": 3})
Pipes¶
A Pipe instance is used to stream data
across runs by associating one given node’s output with another’s input.
In our case, the required pipe is represented by the arrow connecting square’s
result and raise_3’s exponent.
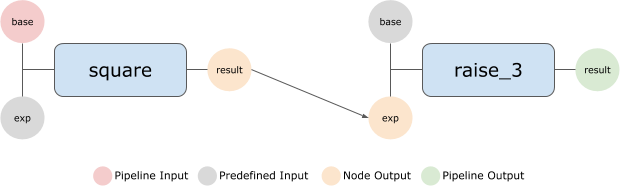
First we create the Pipeline
instance:
>>> from django_analyses.models import Pipeline
>>> pipeline = Pipeline.objects.create(
>>> title="Simple Pipeline", description="A simple pipeline."
>>> )
And then we can lay down the pipe:
>>> from django_analyses.models import Pipe
# Querying the required InputDefinition instances
>>> square_output = exponent_calculation.output_definitions.get(key="result")
>>> raise_3_input = exponent_calculation.input_definitions.get(key="exponent")
# Create the pipe
>>> pipe = Pipe.objects.create(
>>> pipeline=pipeline,
>>> source=square,
>>> base_source_port=square_output,
>>> destination=raise_3,
>>> base_destination_port=raise_3_input,
>>> )